Nature of Heat and Work
Nature of Heat and Work: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Mechanical Work, Work, Heat, Gravitational Work & Electrical Work etc.
Important Questions on Nature of Heat and Work
The generators are also involved in the electrical work done.
The electrical work is due to _____ in metals.
How will you measure the electrical work done?
How does battery related to the electrical work?
Define electrical work done by/on the system.
The gravitational energy can be converted into kinetic energy of an object.
The work done by gravity is given by the formula, . The negative sign shows that the particle is dropping from a height _____ in the direction of gravity.
How does the mass of an object related to the gravitational work?
A box falls at angle from a height of . Express that what kind of work done during the action.
Discuss the gravitational work.
Which energy is a part of mechanical energy?
A heat pump is used to draw water from a well. The temperature of the water is and that of the atmosphere is . If the amount of water drawn is from a depth of , calculate the amount of heat supplied to the well in kJ.
Express your answer up to nearest integer value.
A water heater, operating on a hydrocarbon fuel heats water flowing at the rate of per minute, from to . If the heat of combustion of hydrocarbon is , how much fuel in is consumed per minute? (Specific heat of water is
A reaction proceeds through two paths and to convert .
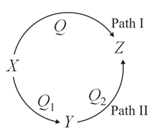
What is the correct relationship between , and ?
For next two question please follow the same
The pressure-volume graphs of various thermodynamics processes are shown:
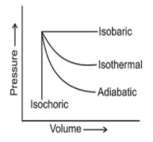
Work is the mode of transference of energy. It has been observed that reversible work done by the system is maximum obtainable work.
wrev > wirr
The works of isothermal and adiabatic processes are different from each other.
If w1, w2, w3 and w4 are magnitude of work done in isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric and isochoric reversible processes, respectively, then the correct sequence (for expansion) would be
In what reaction of the following, work is done by the system on the surroundings?
In a chemical reaction work is done by the system when
Given at , a mole of an ideal gas is isothermally expanded. Now, what is the amount of heat absorbed by the gas until its volume doubled?
At pressure, the air is expanded from to . Now, find the external work done:
Name the system in which there is no exchange of matter, work or energy from surrounding :
